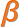It took 16 months to reach half-way, and almost two years to reach two thirds. Speaks volumes for governments’ commitment to sustainability

IN A NUTSHELL
Ratifications of the June 2022 Fisheries Subsidies Agreement
May 13, 2024
Total ratifications = 75
(= 46% of all members, = 68% of the first target)
First target (two thirds of 164 members) = 110
Additional ratifications needed to reach two thirds = 35
Members that have not ratified = 88
Eventual target (agreement applies to all members) = 164 members (or 163 ratifications*)
● The agreement takes effect after two thirds of the membership have ratified (“accepted”) it. Even then it only applies to the countries that have ratified
● The WTO’s up-to-date list of ratifications is here
* So long as the EU’s ratifications count as 27 (the number of EU member states) instead of 28 (member states + EU itself, also a WTO member), total ratifications cannot exceed 163
By Peter Ungphakorn
POSTED JUNE 7, 2023 | UPDATED MAY 14, 2024
June 17, 2023 is already buried in the distant the past. That was the first anniversary of WTO members agreeing by consensus to curb fisheries subsidies. It was also the original target for enough countries to ratify it so that deal could take effect.
That target was then moved to the February 26–29, 2024 Ministerial Conference in Abu Dhabi. When that was going to be missed by a substantial shortfall, the deadline was quietly dropped.
Instead the Ministerial Conference was turned into a celebration of the ratifications that had been submitted, including nine at the conference. That brought the total to 70, still 40 short of the 110 needed to activate the agreement in ratifying countries.
It may take many more months, if not a year or two, to reach 110 — two thirds of the membership. Even then 53 countries will still have not ratified the agreement, meaning it will not apply to them. (Ignoring the likelihood that by then the WTO is likely to have at least two more members.)

COUNTRIES THAT STILL HAVE NOT RATIFIED THE 2022 AGREEMENT
MAY 13, 2024
Afghanistan, Angola, Antigua and Barbuda, Argentina, Armenia, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Benin, Bolivia, Brazil, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Colombia, Congo, Costa Rica, Democratic Republic Congo, Djibouti, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Egypt, El Salvador, Eswatini, Georgia, Ghana, Grenada, Guatemala, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Guyana, Honduras, India*, Indonesia*, Israel, Jamaica, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kenya, Kuwait, Kyrgyz Republic, Lesotho, Liberia, Liechtenstein, Madagascar, Malawi, Maldives, Mali, Mauritania, Mexico*, Moldova, Mongolia, Montenegro, Morocco*, Mozambique, Myanmar*, Namibia, Nepal, Nicaragua, Niger, North Macedonia, Oman*, Pakistan, Panama, Papua New Guinea, Paraguay, Qatar, Saint Kitts and Nevis, St Vincent & the Grenadines, Samoa, Sierra Leone, Solomon Islands, Sri Lanka, Suriname, Taiwan, Tajikistan, Tanzania, Thailand*, Tonga, Trinidad and Tobago, Tunisia, Uganda, Vanuatu, Venezuela, Vietnam*, Yemen, Zambia, Zimbabwe (88)
* In the top 20 fishing nations by catch size (FAO data)
Continue reading “WTO members are slow to ratify the Fisheries Subsidies Agreement”
![]()